As teachers new to Comprehensible Input strategies get their feet wet in the classroom, it’s often helpful to imagine a beginners conversation and script the language use, insuring that the novice-level students don’t get overwhelmed by too many new sounds and words coming in. As teachers gain experience implementing the strategies, they may be able to deliver Hebrew language more improvisationally. But to start, it’s nice to have a road map! Feel free to print and highlight the questions (listed in Hebrew without English how-to commentary at bottom of blog post!), and use them as a loose script, until your own Circling & PQA become more automatic and effortless!
Let’s say that in the interest of laying in the highest frequency Hebrew verbs in order to build a practical foundation in Hebrew, you decide to interview and survey your students about their preferred ice cream flavor, focusing primarily on the verb, אוהב/ אוהבת.

This slide is from my Intro To T/CI presentation on the blog, here.
A series of affirmations, negations, compare & contrast, counting and summarizing questions may ensue, as follows:
T= Teacher; S = Student; Ss = students; C= (whole) Class
NB: All of the parts of the initial statement will be clarified through gesturing, Pause-Point-Slow, sketching, establishing meaning, and ongoing comprehension checks, as discussed and modeled in parts #1 & #2 of this Starting The Year blog post series.
כיתה, אני אוהבת גלידת ׳מוס טרקס.׳
Teacher comes close to next student to interview and addresses him/her by name, looking at her and ‘teaching to the eyes’:
T: זיוה, את אוהבת גלידת ‘מוס טרקס?’
Zivah gestures a thumbs down.
T to Zivah:
?אהההה, את לא אוהבת גלידת ‘מוס טרקס?’
?כיתה, אני אוהבת גלידת ׳מוס טרקס.׳ זיוה לא אוהבת גלידת ‘מוס טרקס, נכון זיוה
The word, ?נכון is a rejoinder. If not already posted because it hasn’t emerged yet, then establish its meaning by writing it on the board, underlining it, and writing it’s English translation below, Correct? -in a contrasting color. Pause-Point-Slow every time you use it, until students demonstrate acquisition by recognizing/using it independently. This may take several sessions.
.זיוה: נכון
Teacher acknowledges Zivah’s comprehension with a high five or fist-bump (‘יש!’) and moves to the next student, or summarizes/contrasts the 2 opinions:
T: .’אני אוהבת גלידת ‘מוס טרקס.’ זיוה לא אוהבת גלידת ‘מוס טרקס
Depending on grade/age and decoding ability, you may decide to leave these as 2 separate (if choppy & short) sentences, for now. Once the incoming message is more effortlessly and automatically understood, you may wish to introduce the conjunction, ‘but’ in context, so simply establish its meaning and restate:
‘.כיתה, אני אוהבת גלידת ‘מוס טרקס’ אבל זיוה לא אוהבת גלידת ‘מוס טרקס
T: ?זיוה, איזה גלידה את אוהבת
Teacher asks with great interest, continuing to gesture, Pause-Point-Slow, and support the conversational language with non-verbal cues. If the student can’t produce a flavor, offer a few cognate flavor choices, as in:
T: ?זיוה, את אוהבת גלידת בננה, או את אוהבת גלידת וניל
Teacher may do a comprehension check here: “What do you think גלידת בננה is?” “What do you think גלידת וניל means?” Acknowledge student comprehension with warmth, smiles, a fist bump (יש!). Though they hopefully don’t feel it, our students’ brains are working hard to understand!
T: !כיתה! זיוה אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה
At that moment you hear a ‘buzz’ in the classroom as other students concur with or differ from Zivah’s choice. You follow the energy and go right to someone you heard who likes or doesn’t like .גלידת שוקולד מנטה
T: !רגע, רגע, רגע
You gesture the Israeli !רגע with one hand, and establish meaning, orally and/or on the board. You walk over to Tammy.
T: ?טמי, את אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה
Tammy shakes her head ‘yes,’ or says, “yes,” or maybe even, “כן.”
You report back to the class, taking care to gesture, pause, and chunk the phrases:
T: .כיתה, זיוה אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה, אבל אני לא אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה
וטמי אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה
C: .הוווווו
T: ? (Point to self) ?ואני כיתה? אני אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה
?’או אני אוהבת גלידת ‘מוס טרקס
C: Moose Tracks.
T: (Expectant pause) ?…נכון, כיתה, נכון. אני אוהבת גלידת ‘מוס טרקס,’ זיוה אוהבת
C: Mint Chocolate!
T: כן, זה נכון! זיוה אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה, וטמי גם אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה
C: !כן
T: What do you think גם means?
T: נכון, גם means ‘also.’
גם זיוה אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה, וגם טמי אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה!
C: הוווווו!
T: ?דניס, גם את אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה
D: .לא
T: ‘?דניס, את אוהבת גלידת ‘מוס טראקס
D: לא
T: ?כיתה! דניס לא אוהבת גלידת ‘מוס טראקס’ וגם לא אוהבת גלידת שוקולד מנטה! הםםםםםםם, דניס את אוהבת גלידת בננה?
At this point (or before!) you may wish to take out a cheat sheet of cognate or borrowed word ice cream flavors from the Israeli ice cream shop menu linked in the previous blog post:
http://www.glidabeersheva.com/%D7%98%D7%A2%D7%9E%D7%99%D7%9D/
D: Salted Carmel.
T: ?או- לה- לה, דניס אוהבת גלידת קרמל! נכון, דניס? את אוהבת גלידת קרמל
D: כן.
T: !כיתה, דניס אוהבת גלידת קרמל
At any natural point the teacher can add an additional rejoinder when she learns new, (EXCITING!) information, as in:
T: ! מקסים! כיתה, דניס אוהבת גלידת קרמל! דניס, זה מקסים
Teacher establishes meaning, writing the Hebrew rejoinder word, underlines it, and in a contrasting color, writes the English word ‘Awesome!’ below it, pausing and pointing every time it comes up in conversation.
Other rejoinders that may work nicely here – but not all at once – use, then post for future use:
!יופי! פנטסטי! סבבה! מצויין
The class carries on as the teacher works her way from student to student, in an unpredictable pattern. While it’s preferable to make sure everyone is interviewed during a single class period, she takes her time, questioning-negating-affirming-comparing:
Comparing students’ preference with each other;
Comparing a student’s preference with her own;
Counting how many prefer a particular flavor (if that happens);
Peppering the banter with rejoinders;
Insuring that she ‘hits her targets’ by including the verb chunk every time -either לא/ אוהב/ת or, if you are starting to branch off the conversation to talk about which flavors have/contain chocolate, then the addition of the verb form יש. (No, it’s not really a verb but it functions as a verb in terms of meaning, and is super hi-frequency!)
T: ?כיתה, יש לגלידת קרמל שוקולד
C: No. (Don’t worry that their response isn’t in Hebrew! We are ascertaining whether they understand the question.)
T: .נכון. אין לגלידת קרמל שוקולד. קרמל זה לא שוקולד, ושוקולד זה לא קרמל
Comprehension check. Possibly write the sentence on the board, depending on decoding skill, and comb through it, establishing meaning as you go.
יש and אין are on one of your hi-frequency posters and subsequently find their place on your Word Wall.
By the end of the class you should be able to surmise everyone’s preferred flavor, and they, each others.’ Depending on the number of Ss, this whole process may take upwards of 20 minutes. We are trying to draw out an engaging conversation, and keep it interesting; we are NOT trying to hurry through in order to extract or list the information. It’s the compelling topic, the repetitions in context, the variations within a narrow set of language, punctuated by rejoinders, fist bumps, smiles and celebration that make this surveying activity so effective in building foundational language.
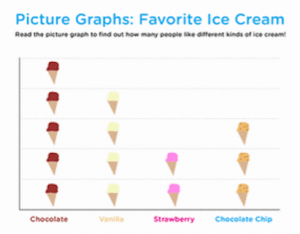
Next class might begin by inserting the collected favorite flavor info into a graphic organizer, in this case perhaps a bar graph with flavors as column titles, and student names sorted into each column. This visual anchor allows us to reconfirm as we build the graph, review, count, sort, compare, and, on the literacy side, decode low stress/hi success names of students and flavors.
For more on using visual anchors read my previous post, Starting the Year #2: Extending CI While Staying In Bounds.
For a copy of the Hebrew only ice cream survey Personalized Questions & Answers (PQA) and Circling script in this article, but without the English ‘How-to’ commentary, click here.




 Summary Of T/CI-Aligned Practices:
Summary Of T/CI-Aligned Practices:






 NOT STRESSED OUT or made to feel inadequate. A high affective filter can be a major obstacle to language acquisition, so we must be vigilant that we aren’t freaking out our kids, or they will tune out and turn off. And researchers will conclude that they are ‘losing their Hebrew language,’ when it’s really the program, itself, that has lost its way.
NOT STRESSED OUT or made to feel inadequate. A high affective filter can be a major obstacle to language acquisition, so we must be vigilant that we aren’t freaking out our kids, or they will tune out and turn off. And researchers will conclude that they are ‘losing their Hebrew language,’ when it’s really the program, itself, that has lost its way.

 But they are, regrettably, also killing student (and teacher) interest and engagement, because the set curriculum is…OK I’ll say it: mind-numbingly boring. Set curricula often ‘covers’ static and humorless topics about which the students are not interested or passionate; nor do many of the themes incorporate the highest frequency words for greatest linguistic coverage.
But they are, regrettably, also killing student (and teacher) interest and engagement, because the set curriculum is…OK I’ll say it: mind-numbingly boring. Set curricula often ‘covers’ static and humorless topics about which the students are not interested or passionate; nor do many of the themes incorporate the highest frequency words for greatest linguistic coverage.


 On Day 4 (our final session) we tried to nail down some logistics, though since we’re rolling out an entirely new program, we will have to tweak it as we go. Some of our challenges are good ones – space is tight, classrooms are full, and we don’t have any spare rooms to dedicate to Hebrew instruction. We’ve already got a workaround as our awesome cantor and 6th grade teacher, Marla, has offered up her (largest) classroom as the dedicated Hebrew room and she will teach in a smaller classroom. Marla says she’s so excited about this new direction for Hebrew instruction that she’s willing to do whatever it takes to make it work!!
On Day 4 (our final session) we tried to nail down some logistics, though since we’re rolling out an entirely new program, we will have to tweak it as we go. Some of our challenges are good ones – space is tight, classrooms are full, and we don’t have any spare rooms to dedicate to Hebrew instruction. We’ve already got a workaround as our awesome cantor and 6th grade teacher, Marla, has offered up her (largest) classroom as the dedicated Hebrew room and she will teach in a smaller classroom. Marla says she’s so excited about this new direction for Hebrew instruction that she’s willing to do whatever it takes to make it work!!